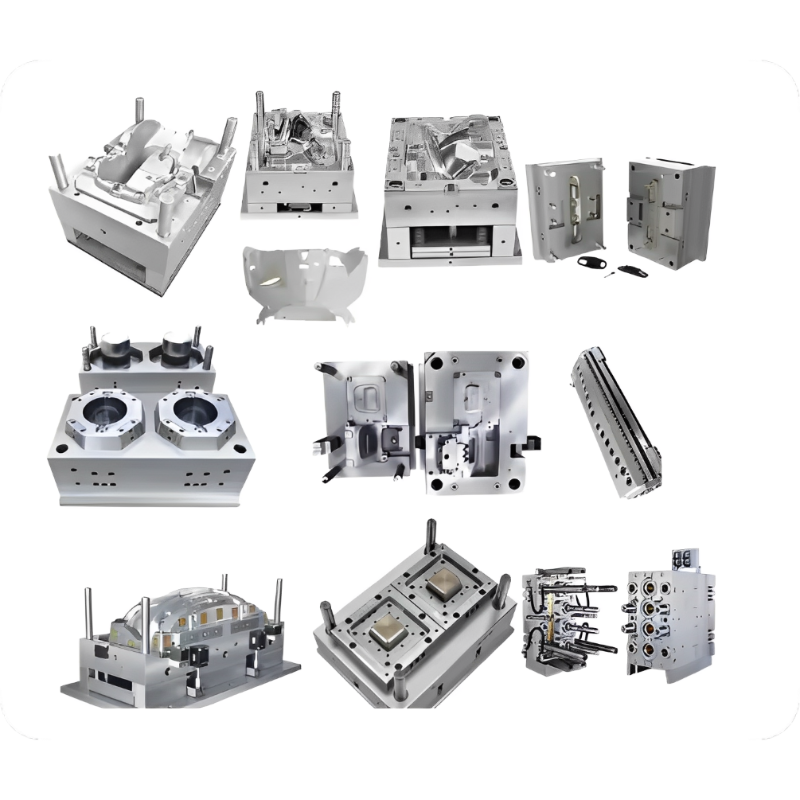
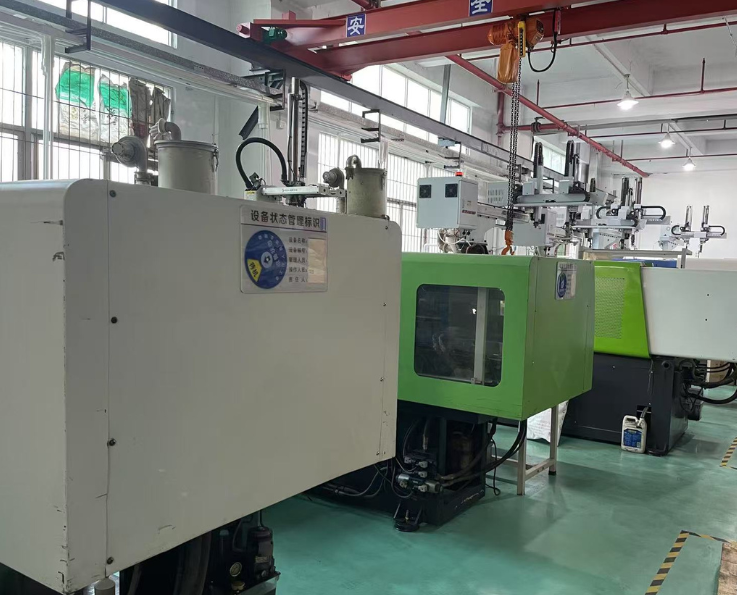
1. What is Injection Molding?
A manufacturing process where molten plastic is injected into a precision mold under high pressure, cooling into a solid part. Key characteristics:
Cycle Time: 10–300 seconds (depending on part complexity)
Tolerances: As tight as ±0.005 mm (medical-grade parts)
Materials: 85% thermoplastic polymers, 12% thermosets, 3% elastomers
Global Market Snapshot:
Valued at 345billion(2023)∗∗,projectedtoreach∗∗512 billion by 2030
Automotive sector dominates (34%), followed by packaging (28%) and electronics (19%)
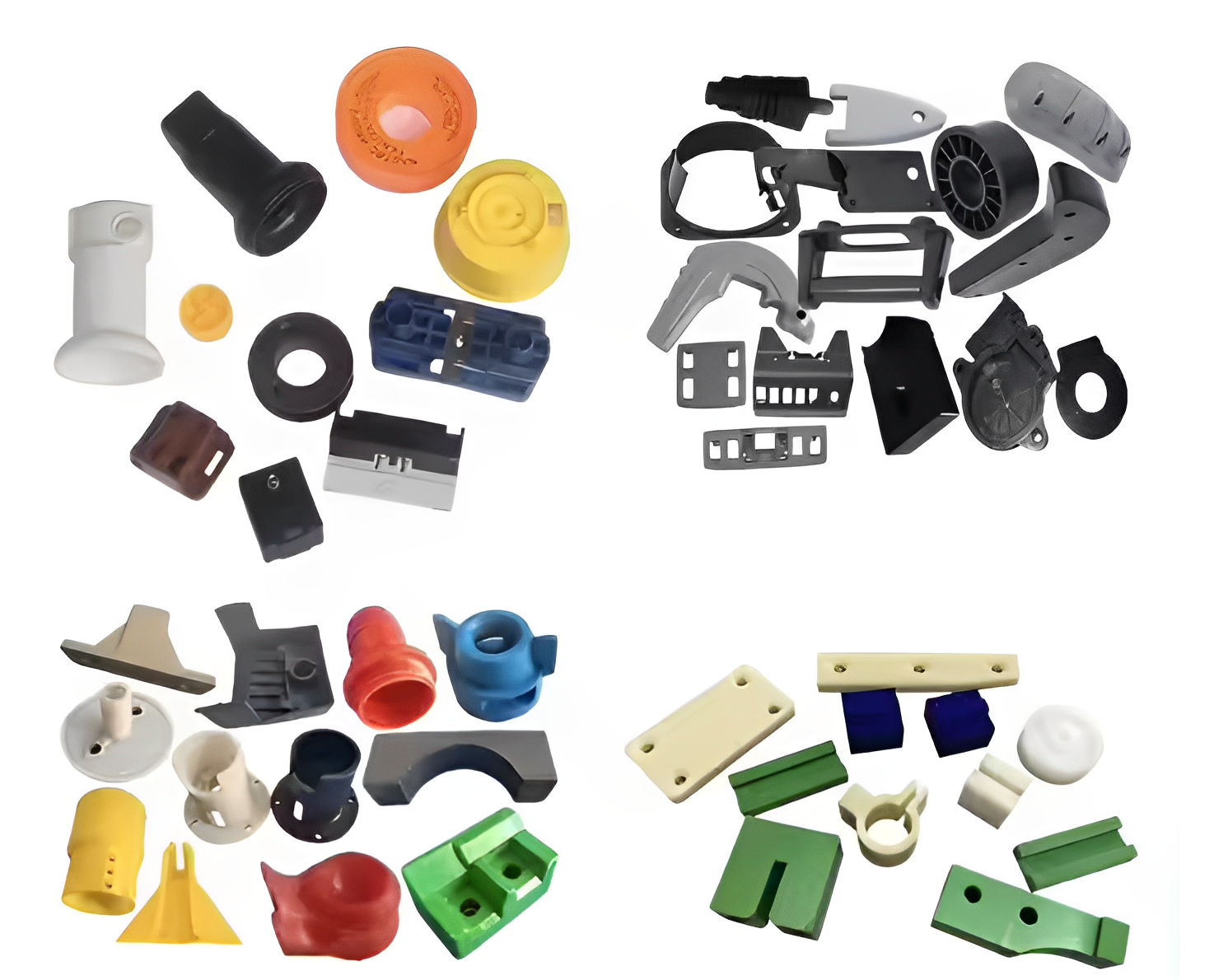

2. The Injection Molding Process: 8 Critical Stages
Stage 1: Material Preparation
Resin Drying: Reduce moisture to <0.02% (e.g., 4 hrs at 80°C for nylon)
Color Masterbatch Mixing: ±1.5% accuracy for consistent pigmentation
Regrind Ratio: Up to 30% recycled material (industry-specific limits)
Stage 2: Clamping
Force: 50–5,000 tons (based on part projected area)
Platen Size: 200 mm × 200 mm to 2,500 mm × 2,500 mm
Parallelism: <0.01 mm/m to prevent flash
Stage 3: Injection
| Parameter | Typical Range | Advanced Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Melt Temperature | 180–320°C (material-dependent) | Infrared thermography |
| Injection Pressure | 500–2,500 bar | Real-time piezoelectric sensors |
| Injection Speed | 50–300 mm/sec | Closed-loop servo control |
Stage 4: Cooling
Conformal Cooling: 3D-printed channels reduce cycle time by 40%
Coolant Types: Water (70%), oil (20%), specialized fluids (10%)
Ejection Temperature: Below material’s heat deflection point
Stage 5: Ejection
Systems: Mechanical pins (80%), air blast (15%), robotics (5%)
Draft Angles: 1°–3° (textured surfaces may require 5°)
Stage 6: Post-Processing
Gate Removal: Laser trimming (±0.1 mm accuracy)
Surface Treatments: IMD (In-Mold Decoration), plasma coating
Assembly: Ultrasonic welding, snap-fit integration
3. Material Selection Matrix
| Material | Melt Temp (°C) | Shrink Rate (%) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | 210–250 | 0.5–0.7 | Automotive trim, LEGO bricks |
| Polycarbonate | 280–320 | 0.6–0.9 | Bulletproof glass, medical devices |
| PEEK | 360–400 | 1.2–1.5 | Aerospace components |
| TPE | 160–220 | 1.5–2.5 | Soft-grip tool handles |
| Bio-PLA | 170–200 | 0.3–0.5 | Compostable packaging |
4. Advanced Injection Molding Technologies
A. Micro-Injection Molding
Part Weight: 0.001–0.1 grams
Applications: Microfluidic chips, hearing aid components
Machines: Electric-driven (0.1 μm screw positioning accuracy)
B. Multi-Material/Overmolding
2K Molding: Bonding TPE to PP in a single cycle
Rotary Platen Systems: 60% cycle time reduction vs. traditional methods
C. Gas-Assisted Molding
Pressure: 100–300 bar nitrogen gas
Benefits: 30% weight reduction, eliminates sink marks
D. Industry 4.0 Integration
AI Quality Control: Deep learning detects 99.98% of defects
Digital Twins: Simulate 50,000 cycles for mold wear prediction
Energy Monitoring: Reduce kWh/kg by 25% via IoT optimization
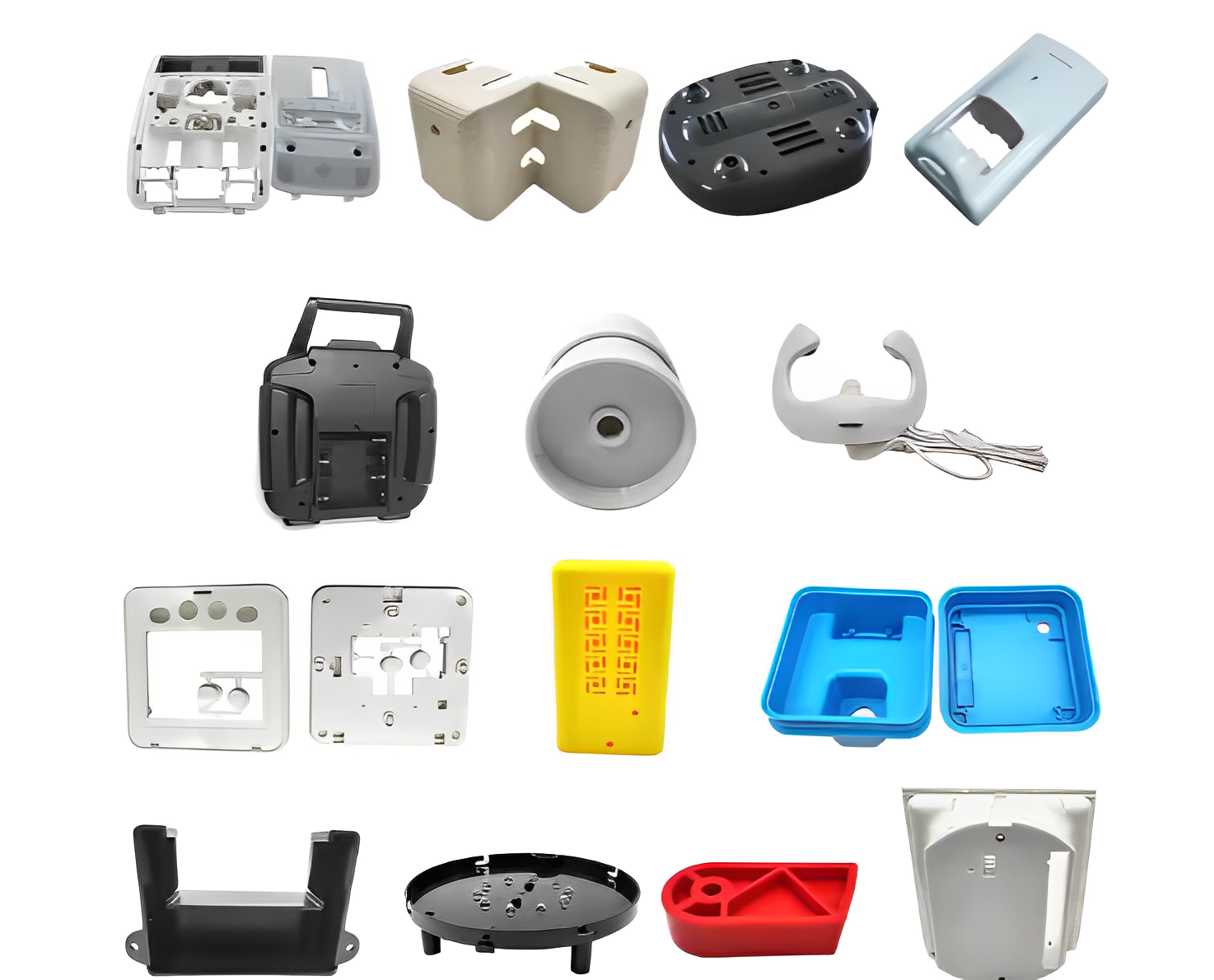

5. Defect Analysis & Solutions
| Defect | Root Cause | Corrective Action |
|---|---|---|
| Sink Marks | Insufficient packing pressure | Increase hold pressure by 15% |
| Flash | Clamping force too low | Raise tonnage or reduce injection speed |
| Short Shots | Material viscosity mismatch | Adjust melt temp ±10°C |
| Warpage | Uneven cooling | Redesign conformal cooling channels |
6. Sustainability in Injection Molding
Circular Economy: 90% regrind reuse in closed-loop systems
Bio-Based Resins: 40% lower carbon footprint vs. conventional plastics
Energy Recovery: Hydraulic systems with 60% energy recapture