In-Depth Guide to Injection Mold Manufacturing: Processes, Technologies, and Applications
Injection mold manufacturing is a cornerstone of modern mass production, enabling the creation of complex plastic components with unmatched precision and efficiency. This comprehensive guide explores every facet of injection mold manufacturing, from design principles to cutting-edge innovations.
1. What is Injection Mold Manufacturing?
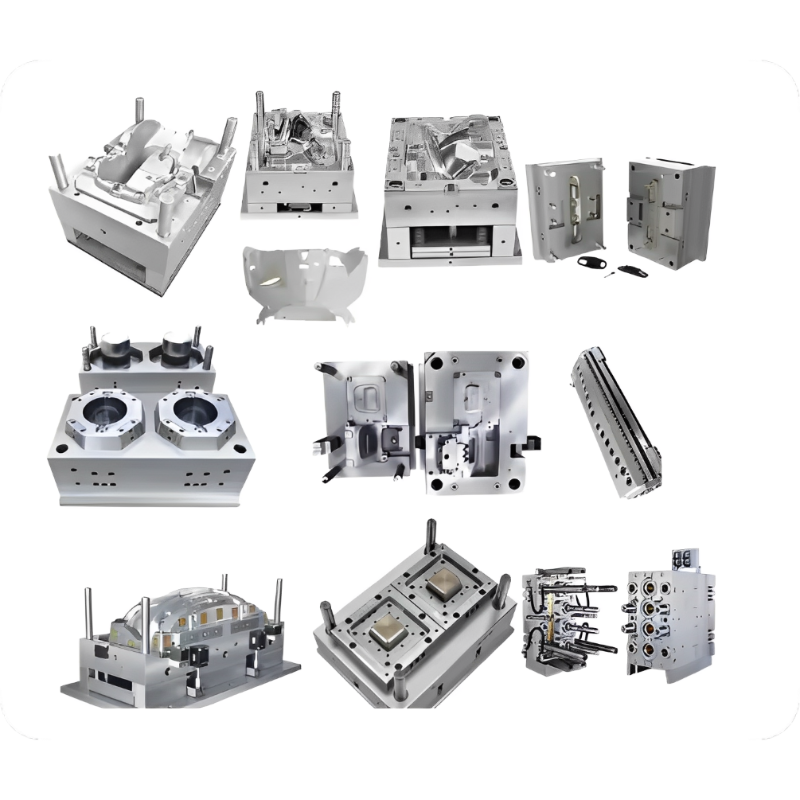
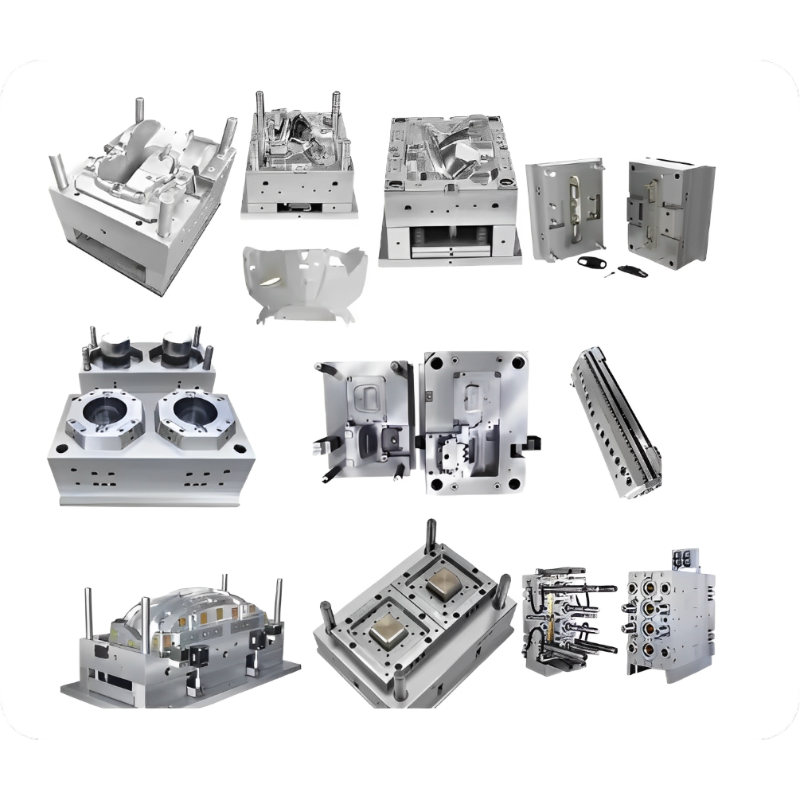
Injection mold manufacturing involves creating custom-designed tools (molds) used to produce plastic parts through the injection molding process. These precision-engineered molds:
Consist of two halves (core and cavity)
Are typically made from hardened steel or aluminum
Contain intricate channels for molten plastic flow and cooling
Determine final part geometry, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy
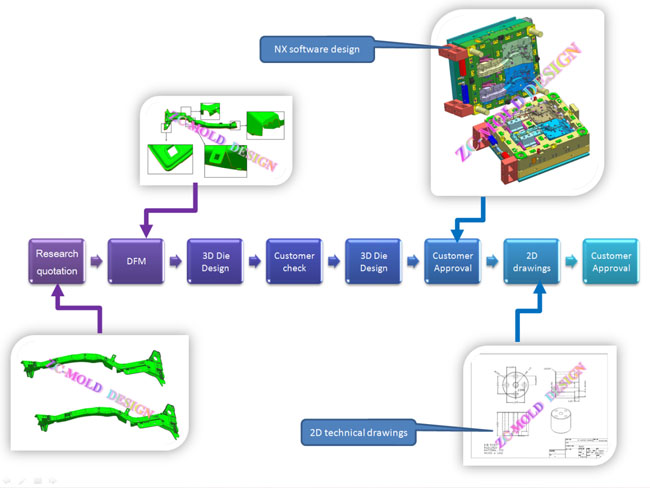
2. The Injection Mold Manufacturing Process: Step-by-Step
Phase 1: Product Design Analysis
DFM (Design for Manufacturability) review
Wall thickness optimization
Draft angle verification (typically 1-3°)
Undercut and ejection system planning
Phase 2: Mold Design Engineering
3D CAD modeling (SolidWorks, UG NX)
Gate type selection (edge, submarine, hot runner)
Cooling system simulation (Moldflow analysis)
Ejection mechanism design (pins, sleeves, stripper plates)
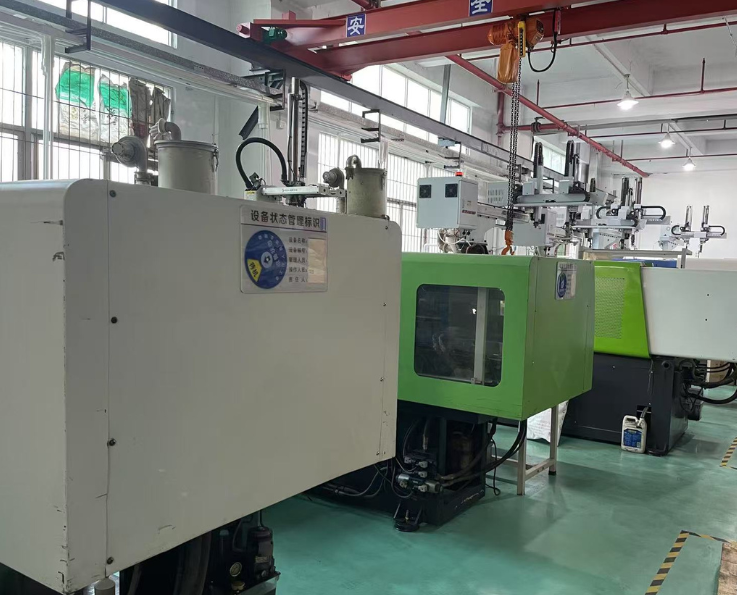
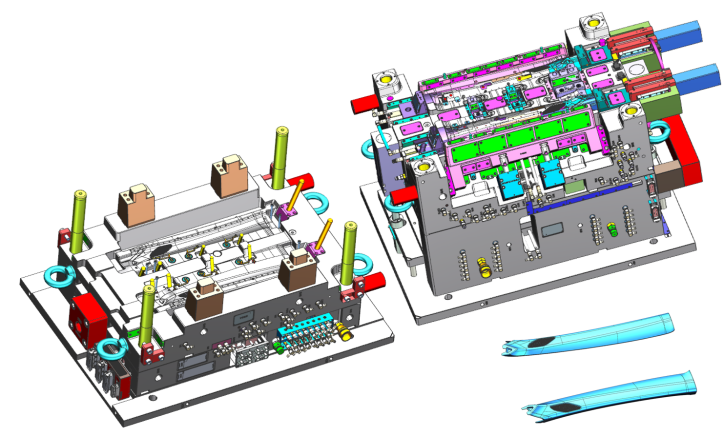
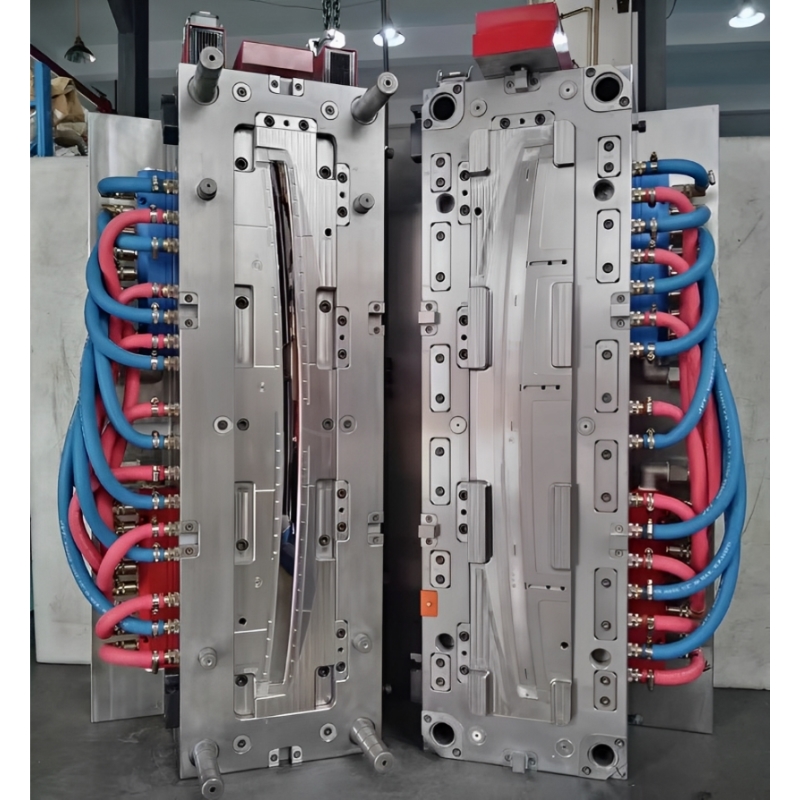
Phase 3: Precision Manufacturing
| Process | Technology | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | 5-axis milling, EDM | ±0.005 mm |
| Heat Treatment | Vacuum hardening (HRC 48-52) | - |
| Surface Finishing | Texturing (VDI 3400 standard) | Ra 0.1-1.6μm |
| Assembly | Guided ejection, alignment systems | ±0.01 mm |
Phase 4: Testing & Validation
T0 Sample Inspection (first-shot parts)
Dimensional checks with CMM
Cycle time optimization
Mold flow analysis verification
3. Advanced Technologies in Modern Mold Making
A. Smart Mold Systems
Embedded sensors for real-time monitoring
IoT-enabled pressure/temperature controls
Self-lubricating components
B. Hybrid Manufacturing
3D printed conformal cooling channels
Laser-cladded wear-resistant surfaces
Micro-milling for optical-grade cavities
C. Sustainable Practices
Recycled tool steel utilization
Energy-efficient mold heating systems
Closed-loop cooling water circuits
4. Material Selection Guide
| Material | Best For | Lifespan (cycles) | Cost Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| P20 Steel | Prototypes, low volume | 50,000-100,000 | |
| H13 Tool Steel | High-volume production | 1,000,000+ | |
| Aluminum 7075 | Rapid tooling | 10,000-50,000 | |
| Beryllium Copper | High thermal conductivity | 500,000+ |

5. Industry-Specific Applications
Automotive:
LED headlight housings (PMMA molds)
Engine intake manifolds (gas-assisted)
Dashboard components (multi-material molds)
Medical:
IV connectors (Class 101 molds)
Surgical instruments (micro-molding)
Implant packaging (clean room compliant)
Consumer Electronics:
Smartphone casings (mirror-finish cavities)
Waterproof connectors (overmolding)
Thin-wall battery covers (<0.5mm)